“I had a beautiful dream today, a really beautiful dream”
So many songs, poems, and scientific publications have been written about sleeping that it would be reasonable to say that we know almost everything about sleep. Does sleep affect our weight? What happens to the body when we provide it with too little of it?
Abstract:
- Lack of sleep leads to an increase in appetite – and therefore to being overweight.
- Insufficient rest causes the metabolism to slow down.
- Lack of sleep affects mental health.
- Melatonin regulates the biological clock.
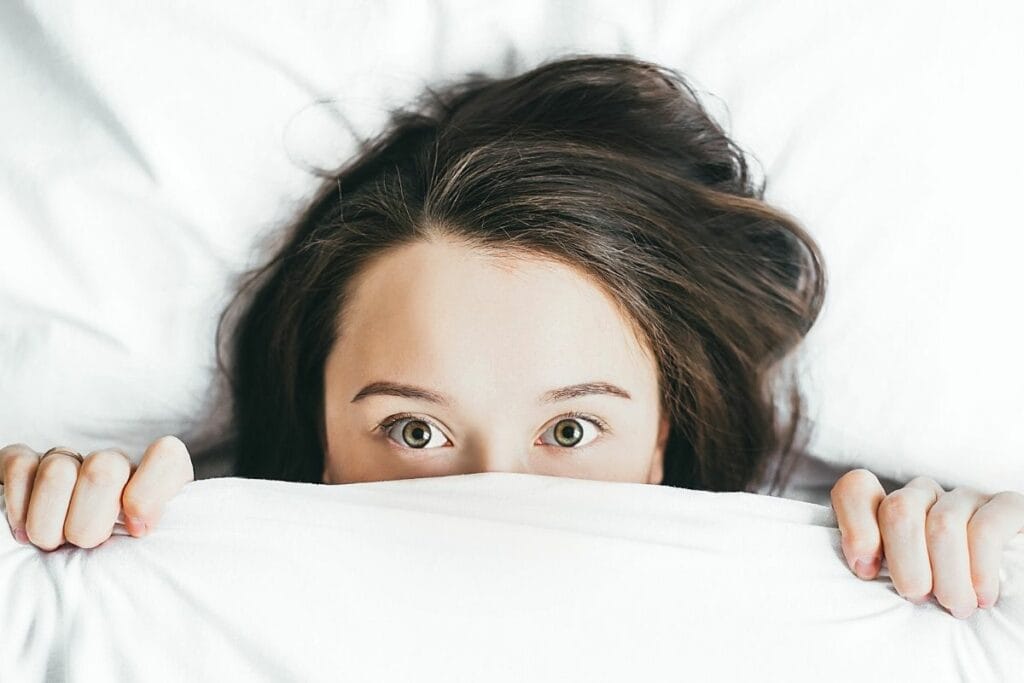
You have to go to sleep before you feel like eating
An adult needs an average of 6-8 hours of sleep per night to maintain adequate levels of rest, as well as broadly defined well-being.
What’s more, according to scientists, by decreasing levels of leptin – the hormone responsible for suppressing appetite – during sleep, and increasing the ghrelin hormone – which in turn is responsible for increasing the appetite – we can prove that sleep has a direct impact on excess weight and obesity for a simple reason – when we are sleep deprived, we are hungry. A drop in leptin levels simultaneously leads to a slower metabolism.
If we lead a lifestyle that avoids sleep, our bodies are more likely to reach for calorie-dense, often highly processed foods to quickly replenish the needs of our alert body. This is an illusory feeling linked to fluctuations in hormone levels which, through insufficient sleep, in a way deceive our body. SUPERSONIC Food Powder is part of a healthy lifestyle, but with the right amount of sleep or physical activity.
What is the risk of sleep deprivation?
Fatigue, sleepiness, difficulty concentrating – we all know them. It has happened to all of us more than once or twice that we have slept far too little or not at all. The reasons range from working, to young children, to an engaging book that was a pleasure to read until dawn.
Initially, inadequate amount of sleep leads to poor mental and physical well-being. Cognitive dysfunction appears shortly thereafter. We are unable to remember a few numbers, we lose our ability to analyse and concentrate.
In the long term, we become susceptible to coronary heart disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes and even premature death.
We must not forget mental health either, as we become more prone to depression and anxiety as a result.
It is well known that playing sports triggers a release of endorphins. Their effects are felt longer after playing sports than after eating chocolate. It has been proven that significant sleep deprivation causes people to give up physical activity. This is just a small step away from crossing the border of a positive energy balance.
In addition, a well-rested body fights infections better.
Melatonin and its effects
Melatonin is a hormone produced in the pineal gland and its function is to regulate the biological clock. It is most often associated with sleeping, and rightfully so, as it is known as the ‘sleep hormone’. Its synthesis occurs in the dark, through closed eyelids.
Among other things, melatonin influences the female monthly cycle by affecting gonadotropic hormones, and this influence can be observed through delayed sexual maturation.
Its adequate level also reduces the risk of cancer, lowers blood pressure, regulates lipids and has an analgesic effect!
The impact of sleep on diet and health is undeniable. Prolonged sleep deprivation can have unpleasant consequences, becoming a direct and indirect threat to health or life. Therefore, if we want our body to function properly, to reduce the risk of contracting serious diseases, but also to make the diet effective and not counterproductive – we should get enough sleep.
Bibliography